科研动态
科研进展丨唐丹玲团队揭示吕宋海峡海域海气相互作用下叶绿素a浓度对台风“风泵”和黑潮共同作用的响应

有研究表明台风风泵引起上升流和冷涡经常促使台风后浮游植物显著增长,也有研究表明台风能引起吕宋海峡海域的黑潮入侵增强,目前黑潮入侵对南海东北部的生态效应(促进还是抑制)尚不明确,更需要探讨台风影响下黑潮入侵对上层海洋叶绿素a浓度(Chl-a)影响。另外,海气热通量交换与上层海洋过程密切相关,台风条件下上层海洋海气相互作用在Chl-a变化中的作用也尚待研究。
该研究利用航次温盐和Chl-a数据、Argo温盐剖面、遥感数据及HYCOM模式数据,以南海2015年台风“莲花”为例,探讨了台风“风泵”和黑潮共同作用下真光层内Chl-a分布的变化及其成因。
1)南海东北部在台风过境1周后,表层(0-50 m)和次表层(50-75 m)Chl-a增加主要是浮游植物的繁殖增长;
2)台风过境1周后引起呂宋海峡西北侧南海海域(A区)甩涡流态的黑潮入侵,该甩涡流套使原有的气旋冷涡的上表层气旋流场结构消失,抑制了台风产生的上升流(艾克曼抽吸和涡致抽吸)对表层(0-50 m)营养盐的供给,使次表层(60-90 m)营养盐富集,进而抑制了表层的Chl-a增长、促进了次表层Chl-a的增长;
3)台风后,虽然吕宋海峡西侧海域(B区)艾克曼抽吸较弱,但由于吕宋海峡西侧海域(B区)位于台风增强的甩涡流套的黑潮入侵路径的西侧,黑潮流场诱发了该海区持续增强的气旋冷涡,该冷涡的涡致上升流(较之于风致艾克曼抽吸)主导了该海区0-50 m的Chl-a显著增长;
4)在吕宋海峡西南侧海域(C区),台风破坏反气旋暖涡,使强艾克曼抽吸产生的上升流更易于将低层营养盐输运到表层,促进上表层(0-50 m)的Chl-a显著增长;
5)在台风增强黑潮入侵的海区,台风过境1周内海气热交换对上层海洋水动力过程的贡献甚至能达到近80%,并通过引起海表降温而间接调控Chl-a增长。
唐丹玲团队长期研究“风泵”的海洋环境和生态效应,承担了国家自然科学基金重点项目“海洋浮游植物粒径组成分布及其相关生态因素对台风的响应---基于遥感与现场观测资料的研究”(41430968)。论文全文链接为:
1. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969720338110?via%3Dihub
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342274164_A_case_study_of_Chlorophyll_a_response_to_tropical_cyclone_Wind_Pump_considering_Kuroshio_invasion_and_air-sea_heat_exchange
2. http://www.lingzis.com/journal%20article.htm
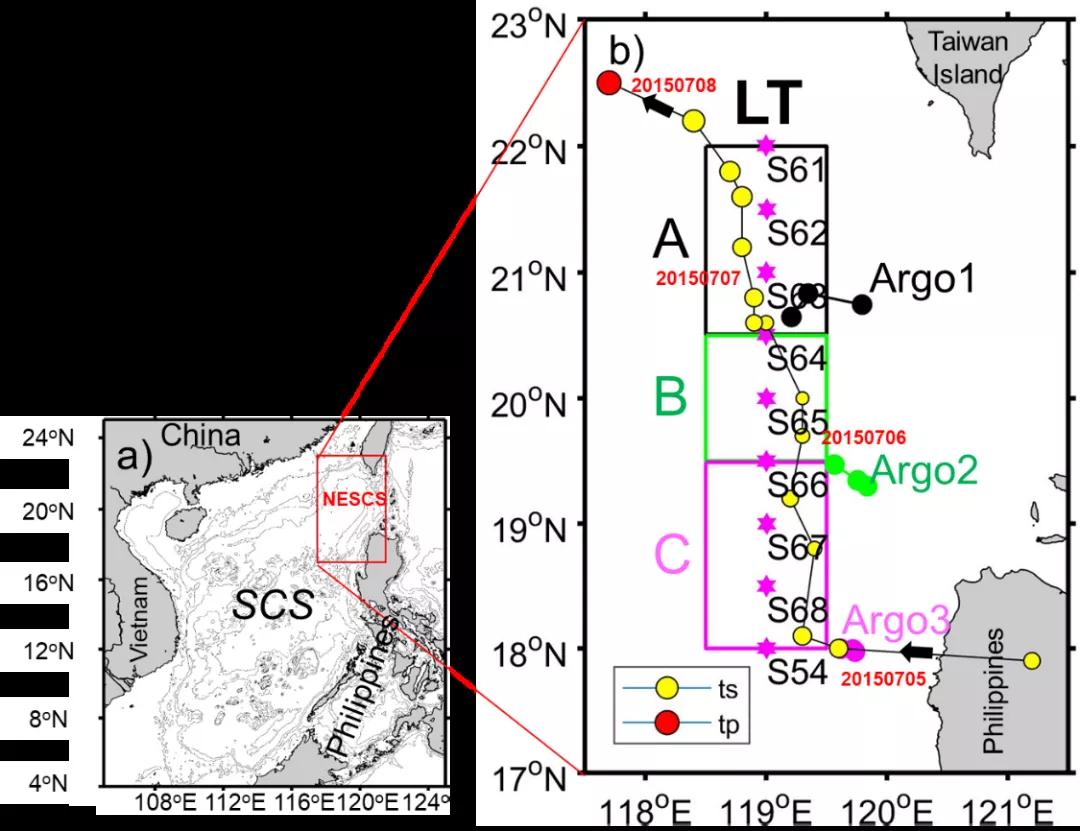
研究区域和热带气旋路径图
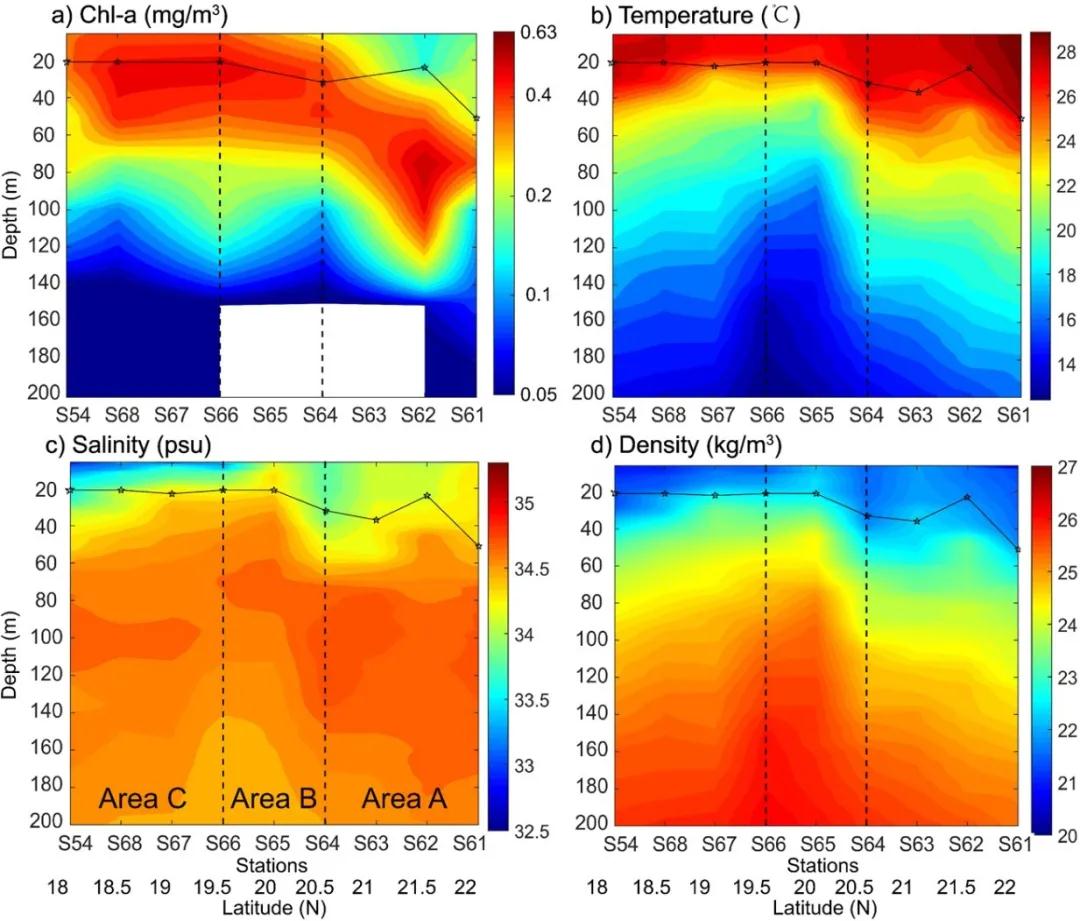
台风过境一周后实测叶绿素a浓度、温度、盐度和密度剖面分布
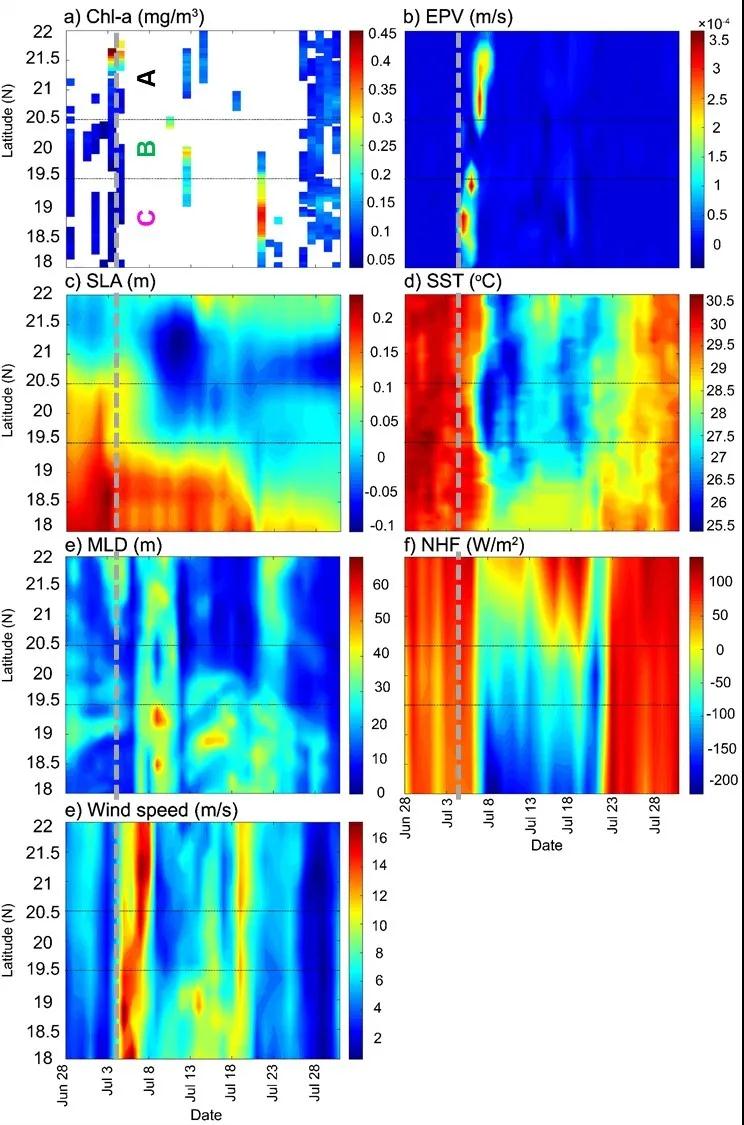
各要素台风前后119°E断面的时空分布
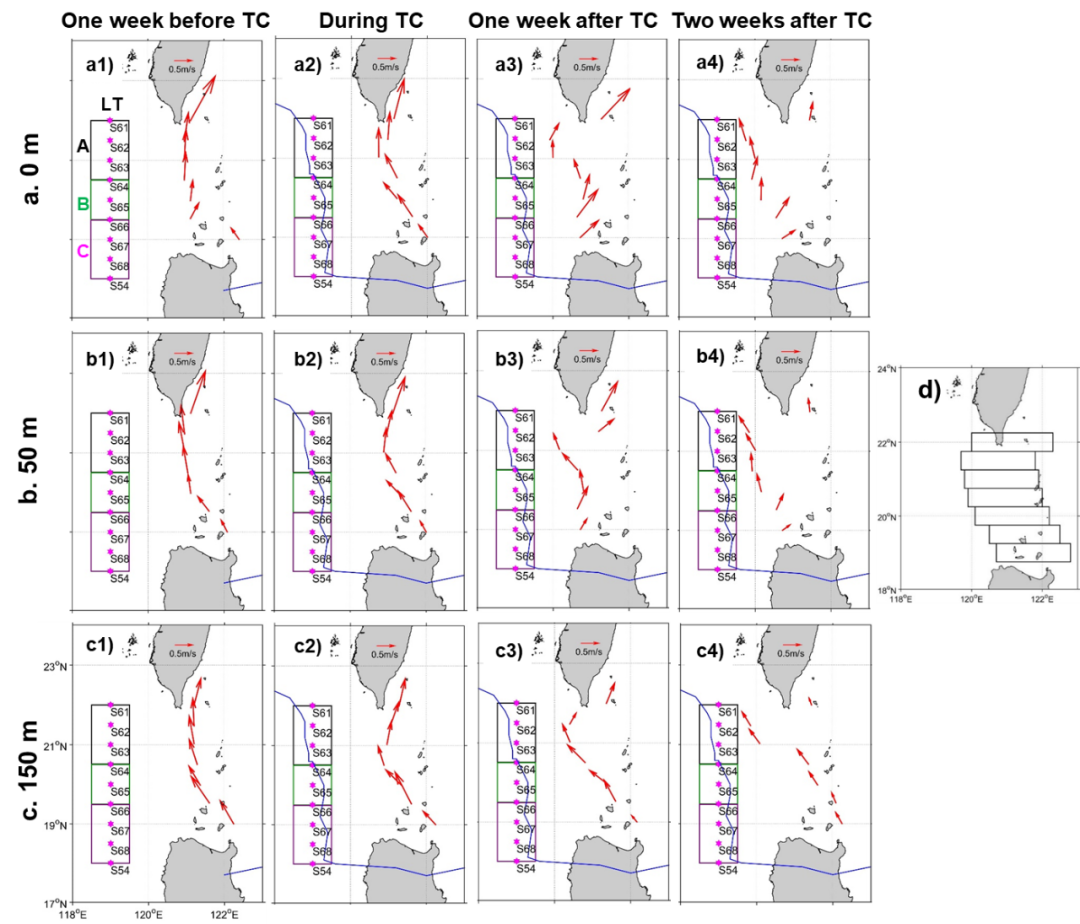
台风前后黑潮流轴的时空分布

机理示意图
本论文引用格式:
Yupeng Liu, Danling Tang*, Shilin Tang, Evgeny Morozov, Wenzhao Liang, Yi sui. A case study of Chlorophyll a response to tropical cyclone Wind Pump considering Kuroshio invasion and air-sea heat exchange. Science of the Total Environment. 2020, 741; doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140290
相关研究参考文献(详见http://www.lingzis.com/journal%20article.htm):
1. HaiJun Ye, Evgeny Morozov, DanLing Tang*, Sufeng Wang, Yupeng Liu, Ying Li, Shilin Tang. Variation of pCO2 concentrations induced by tropical cyclones “Wind-Pump” in the middle-latitude surface oceans: a comparative study. PLOS ONE, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0226189
2. Yupeng Liu, Danling Tang * and Morozov Evgeny , 2019. Chlorophyll concentration response to the typhoon Wind-Pump induced upper ocean processes considering air-sea heat exchange, Remote sensing. 2019, 11, 1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11151825
3. Huabing Xu, Danling Tang*, Yupeng Liu,Ying Li.2019. Dissolved oxygen responses to tropical cyclones "Wind Pump" on preexisting cyclonic and anticyclonic eddies in the Bay of Bengal. Marine Pollution Bulletin. 146 (2019) 838–847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.07.019
4. 孙庆杨, 林静柔, 唐丹玲, 等. 南海海气CO2 交换对两个热带气旋“风泵”的不同响应机理分析[J]. 生态科学, 2020, 39(3): 9–16. https://doi.org/10.14108/j.cnki.1008-8873.2020.03.002
5. Huabing Xu, Danling Tang*, Jinyu Sheng, Yupeng Liu, Yi Sui, 2019. “Study of dissolved oxygen responses to tropical cyclones in the Bay of Bengal based on Argo and satellite observations”, Science of the Total Environment. Volume 659, 1 April 2019, Pages 912-922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.384
6. Haijun Ye, Jinyu Sheng, Danling Tang*, Eko Siswanto, Muhsan Ali Kalhoro, Yi Sui., 2017. “Storm-induced changes in pCO2 at the sea surface over the northern South China Sea during Typhoon Wutip”. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/2016JC012643
7. HaiJun Ye, Jinyu Sheng, Danling Tang*, Evgeny Morozov, Muhsan Ali Kalhoro, Sufen Wang, Huabing Xu. 2019. Examining the impact of tropical cyclones on air-sea CO2 exchanges in the Bay of Bengal based on satellite data and in-situ observations, Journal of Geophysical Research-Oceans. Volume124, Issue1, January 2019, Pages 555-576. http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2018JC014533
8. Sun, Q., D. L. Tang, L. Legendre, and P. Shi (2014), Enhanced sea-air CO2 exchange influenced by a tropical depression in the South China Sea, J. Geophys. Res. Oceans, 119. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JC010131
9. Ye H J, Sui Y, Tang D L, et al. A subsurface chlorophyll a bloom induced by typhoon in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2013, 128:138-145. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2013.04.010
10. Jie Yu , Danling Tang, Yongzhen Li , Zirong Huang, Guobao Chen,2013,Increase in fish abundance during two typhoons in the South China Sea,Advances in Space Research. 51(2013):1734-1749. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2012.11.019
11. Yongqiang Chen & Danling Tang (2012): Eddy-feature phytoplankton bloom induced by a tropical cyclone in the South China Sea, International Journal of Remote Sensing, 33:23, 7444-7457. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2012.685976
12. Zheng, GM,Tang, DL. Offshore and nearshore chlorophyll increases induced by typhoon winds and subsequent terrestrial rainwater runoff[J]. MARINE ECOLOGY-PROGRESS SERIES,2007,333:61-74. http://dx.doi.org/10.3354/meps333061
