科研动态
科研进展丨北印度洋环境变化下剑鱼的中上层栖息地研究
第一作者Thushani Suleka Madhubhashini Elepathage 是唐丹玲研究员的博士研究生,来自斯里兰卡。
Abstract:

Swordfish (Xiphias gladius) are a highly migratory keystone species, found in tropical and temperate seas that are influenced by environmental parameters. In the Bay of Bengal, the Arabian Sea, and the ocean region around Sri Lanka, the environment is gradually changing as a result of climate change. In this study, we identified the preferable environmental conditions for swordfish using satellite-derived environmental data and in-situ fish catch data. We modeled the relationships between fish distribution and the environment changes using Boosted Regression Trees (BRT) and Generalized Additive Model (GAM) methods. The monthly mean fishing effort is comparatively high from October to March and the fish catch rates are high from September to November. Chlorophyll-a concentration has a positive relationship with catch rates while sea surface temperature (SST), sea salt surface mass concentration (SSS), and effort show negative relationships. Approximately 0.3–0.4 mgm?3 of chlorophyll-a, 28–28.5 °C SST, and (3–5)10?8 kgm?3 of SSS were significantly correlated with high swordfish catch rates. According to the optimum environmental conditions identified using the above models, the suitable environmental spatial and temporal distribution was mapped. The results show that the optimum conditions for swordfish are in the eastern region of Sri Lanka, around Thailand and Myanmar, from June to August, and around Bangladesh, Myanmar, Pakistan, the west coast of Sri Lanka, and the east coast of India during September to November.
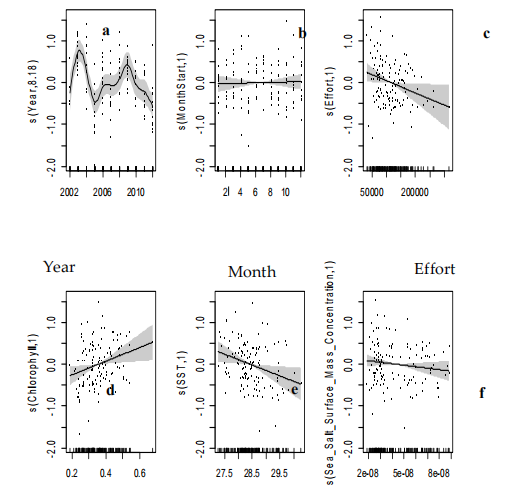
Modeled effect of (a) year, (b) month, (c) effort, (d) Chlorophyll-a, (e) SST, and (f) sea surface salt (SSS) mass concentration on swordfish catch rates in the study region. The black solid line indicates the fitted GAM function and the ash color area indicates 95% confidence intervals. The relative density of data points is shown by the rug plot on the x-axis and the data are indicated by black dots.
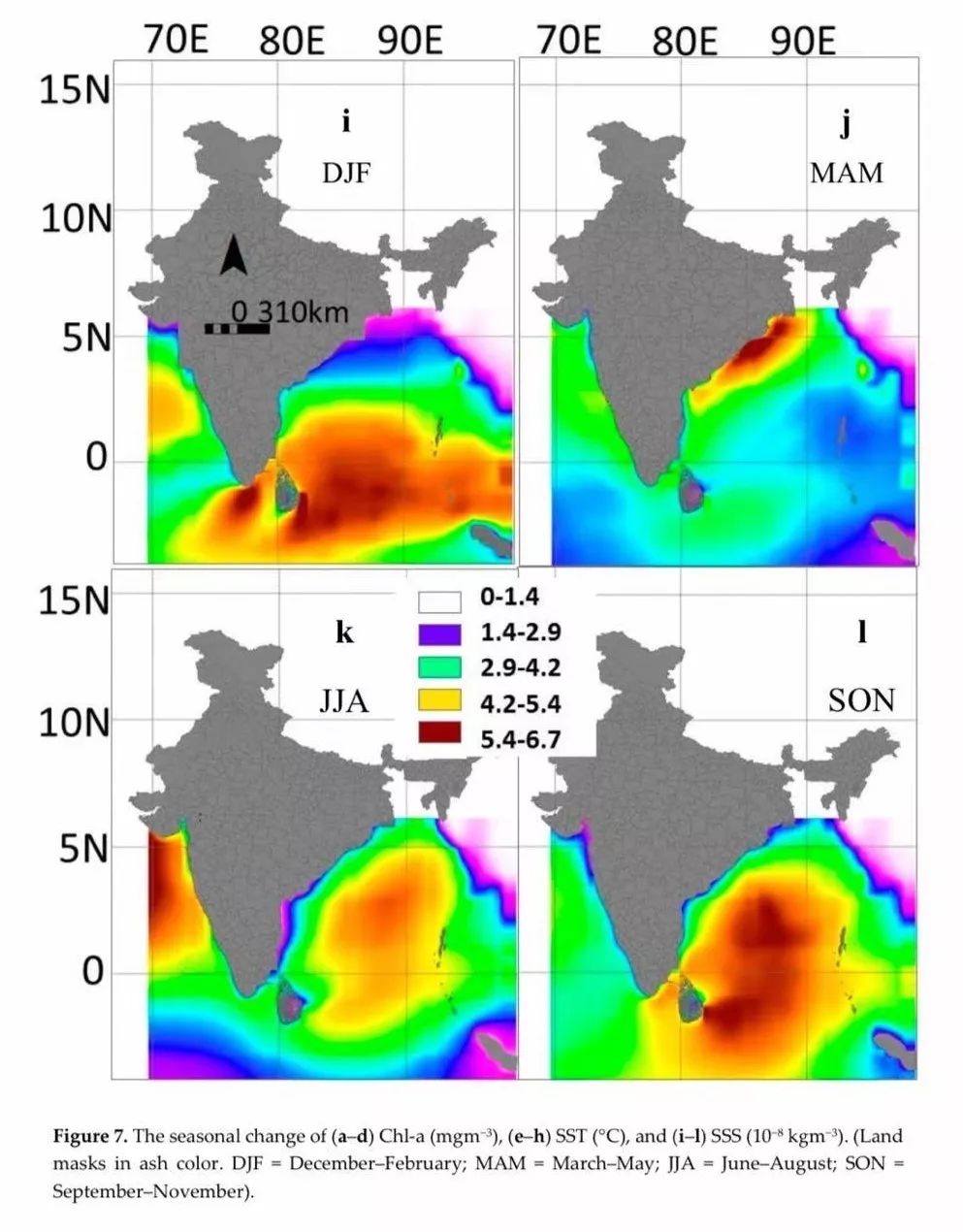
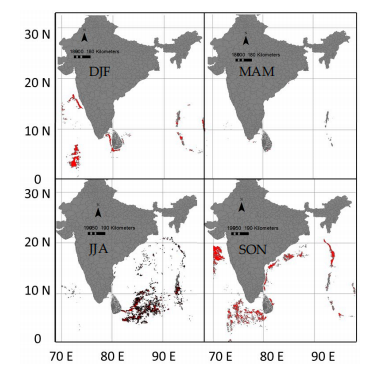
The pelagic habitat of swordfish according to the distribution of optimum environmental conditions. (Habitats are demarcated in red; land masks are indicated with an ash color.).

This research was funded by National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (41430968, 41876136). Collaborative Innovation Center for 21st-Century Maritime Silk Road Studies, Guangzhou, China(21世纪海上丝绸之路协同创新中心,海洋资源开发与海洋经济合作研究) (2015HS05), Chinese scholarship council (2015HS05), Prince Albert II foundation in Monacco and Key Special Project of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou).
本文信息
Thushani Suleka Madhubhashini Elepathage, Danling Tang*, and Leo Oey.2019. The Pelagic Habitat of Swordfish (Xiphias gladius) in the Changing Environment of the North Indian Ocean. Sustainability 2019, 11, 7070; doi:10.3390/su11247070 2019
2019年唐丹玲团队印度洋海洋生态环境和渔业资源研究的部分相关论文:
-
Huabing Xu,Danling Tang*, Yupeng Liu,Ying Li. 2019. Dissolved oxygen responses to tropical cyclones "Wind Pump" on preexisting cyclonic and anticyclonic eddies in the Bay of Bengal. Marine Pollution Bulletin. 146 (2019) 838–847
-
Thushani Suleka Madhubhashini Elepathage,Danling Tang*, 2019,Hydroclimatic changes analysis with remote sensing data in Sri Lankan waters, Journal of marine biology and oceanography. 2019, 8:1
-
Huabing Xu,Danling Tang*, Jinyu Sheng, Yupeng Liu, Yi Sui, 2019. “Study of dissolved oxygen responses to tropical cyclones in the Bay of Bengal based on Argo and satellite observations”, Science of the Total Environment. Volume 659, 1 April 2019, Pages 912-922
-
HaiJun Ye, Jinyu Sheng,Danling Tang*, Evgeny Morozov, Muhsan Ali Kalhoro, Sufen Wang, Huabing Xu. 2019. Examining the impact of tropical cyclones on air-sea CO2 exchanges in the Bay of Bengal based on satellite data and in-situ observations, Journal of Geophysical Research-Oceans. Volume124, Issue1 , January 2019, Pages 555-576. DOI: 10.1029/2018JC014533
……
PDF原文获取:
1. http://www.lingzis.com/journal%20article.htm(#151)
2. https://www.mdpi.xilesou.top/2071-1050/11/24/7070
